Logistics is an integral part of our daily lives, often operating behind the scenes to ensure that products and services are delivered seamlessly. Whether it's the food we purchase at the grocery store, the latest gadget ordered online, or the fuel in our cars, logistics plays a crucial role in making these everyday conveniences possible.
Take, for example, the journey of fresh produce to your local supermarket. Fruits and vegetables are harvested, processed, and transported under strict conditions to preserve freshness. They travel through a network of trucks, warehouses, and retail stores, orchestrated with precision to ensure they reach you in peak condition. Another vivid example is the logistical marvel behind Amazon. When you click 'Buy' on an Amazon product, a complex system is set into motion. The item is picked from a warehouse, often by robots, then transported via a series of trucks and planes, coordinated by advanced algorithms to ensure it reaches you in just a day or two.
The logistic industry is changing minute by minute; therefore, being updated with knowledge on logistics trends in 2024 becomes very essential for staying ahead in business. This article reveals the top trends for logistics in 2024-2025 and the most newsworthy innovations that are revolutionizing this sector's future.
IoT in logistics
The Internet of Things refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data over the internet. IoT in logistics is working to transform the industry by facilitating real-time data exchange and automation. The expected growth in IoT connections, projected to rise from 19.5 billion in 2025 to 40.1 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 16%.
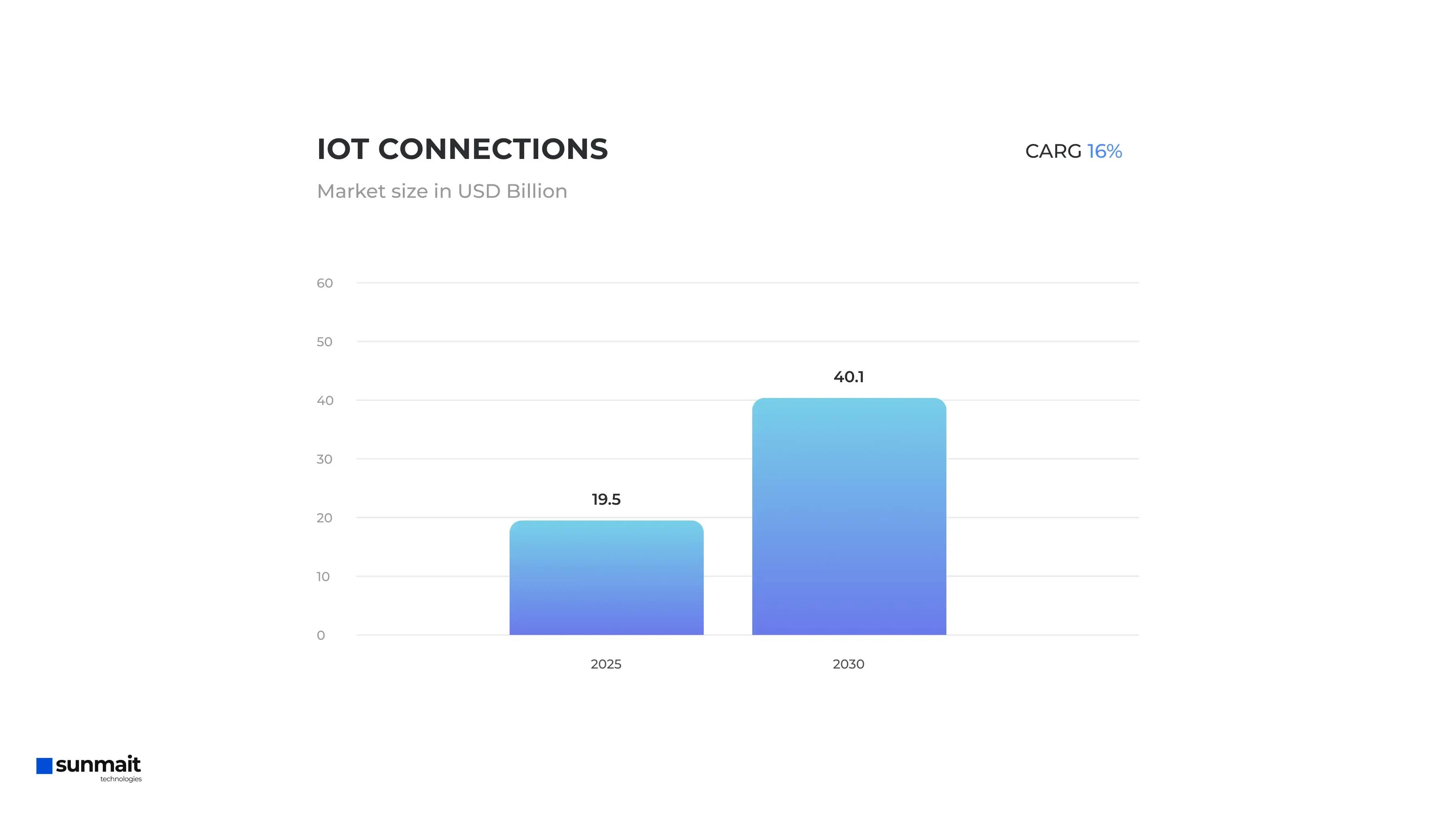
Expected growth in IoT
Source of data: ABIresearch
From the warehouse to your doorstep, a parcel is traceable using IoT devices. Inventory within the warehouse is handled by smart sensors, and GPS trackers provide real-time location updating for the parcel. It integrates IoT into logistic procedures, making inventory control easier to monitor and manage.
During transportation, IoT sensors in a vehicle continuously send performance data for the prediction of maintenance needs, thereby contributing to avoiding breakdowns. This enables on-time deliveries and helps minimize disruptions. Now, when this package reaches the local distribution center, RFID tags will do their job: They enable sorting and routing without errors, increasing the speed of delivery.
The use of AI and ML in logistics
AI in the supply chain and logistics drives data-driven decisions and automates highly complex processes. Starting from demand forecasting to route optimization, AI in logistics is proficient in enhancing efficiency and responsiveness. Those technologies smoothen operations, improving every single aspect of the supply chain.
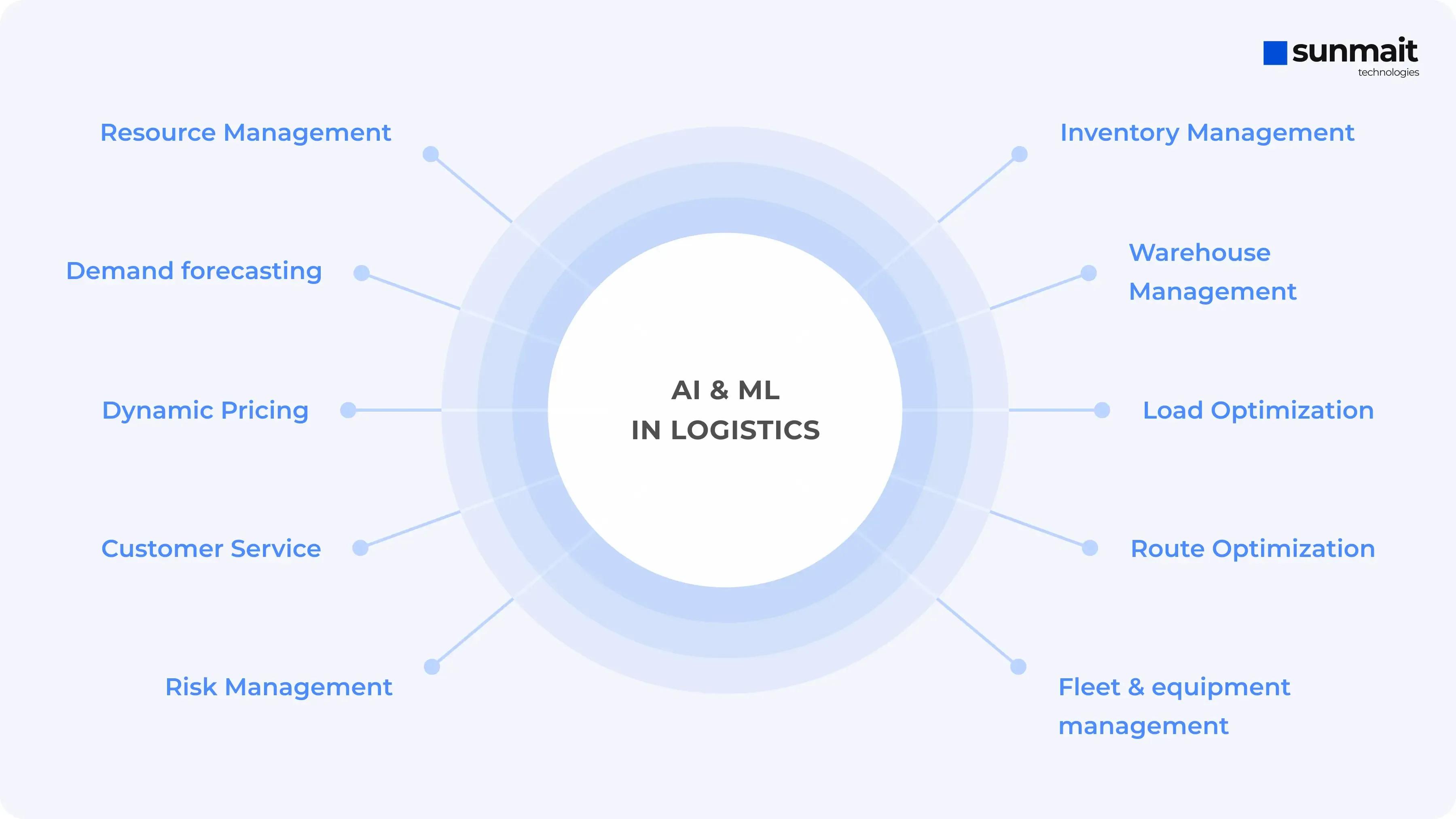
AI and ML in logistics
Here’s how they impact a single supply chain:
Demand forecasting is where the supply chain must begin. AI in supply chain and logistics assumes a significant role: AI and ML algorithms go deep into the analysis of historical sales data and market trends to come up with a forecast of future demand with high accuracy. Such a system would help a company maintain optimal inventory levels, avoiding overstock and stock-outs. Since this would project fluctuations in demands, businesses would stand at a better position to adjust production schedules and procurement strategies.
Resource Management: Next, AI in logistics optimizes resource allocation by analyzing workload data, such as order volumes and processing times.This ensures tasks are efficiently distributed among workers, maximizing productivity and minimizing delays. For instance, during peak seasons, AI can dynamically reassign tasks to handle increased order volumes.
Inventory Management: AI helps managers of supply chains accurately calculate the optimal inventory level, recognize slow-moving products, and project excess inventory that might occur in the future. This enables them to manage stock effectively, cutting holding costs and reducing waste. Real-time inventory visibility offers the opportunity for much quicker reactions to changes in the marketplace.
Warehouse Management: At the warehouse level, AI-driven technologies are changing item placements dynamically according to previous data and current demand. Digital twins optimize layouts and workflows by creating a 'virtual twin.' Automated systems, handling picking, packing, and sorting, are automated to drive accuracy and efficiency. AI, paired with digital twins, ensures that workers travel the least distance to their respective racks for pickup, ensuring space and resources are utilized effectively.
Load Optimization: As goods are prepared for shipment, AI optimizes the allocation of items to trucks or containers, considering factors such as weight, volume, and route efficiency. This ensures maximum utilization of available space and reduces transportation costs. AI in supply chain and logistics adapts to real-time changes, helping teams quickly adjust for disruptions or new orders
Route Optimization: Artificial intelligence analyzes historical and real-time data, such as traffic patterns and climate, among other relevant factors, to understand which route would be best for transportation to determine the best routes for delivery. This reduces fuel consumption and delivery time, increasing efficiency. For example, at any given time, AI can reroute drivers to avoid traffic.
Fleet and equipment management: En route, AI and ML make predictions about potential issues with vehicles or equipment, such as maintenance needs or fuel costs. This proactive method allows for effective repair, reducing downtime and extending life.
Risk Management: ML-based models assess the supply chain's readiness for unforeseen events, minimizing disruptions and enhancing resilience. Driver scorecards monitor behavior like speeding and harsh braking, improving safety and compliance. AI estimates border and customs wait times, suggesting optimal departure times to avoid delays. It also analyzes truck sensor data to select the best vehicle for each task, reducing the risk of breakdowns.
Customer Service: Upon approaching delivery, AI-powered chatbots handle customer inquiries and provide real-time updates on order and shipment status. This improves customer experience by offering instant support and freeing up human resources for more complex tasks. Chatbots can also assist with returns and refunds, streamlining the process.
Dynamic Pricing: Throughout the process, AI uses historical and real-time data to anticipate shipping costs and adjust prices dynamically. This ensures competitive pricing while maintaining profitability. For example, AI can factor in current fuel prices and demand levels to set optimal shipping rates. Dynamic pricing serves to ensure customers get services even when demand exceeds supply, while at the same time, it efficiently allocates resources.
In short, AI and ML improve logistics by impacting every stage. These technologies increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve service quality throughout the supply chain.
Robotics and Automation
Imagine a modern warehouse that is busy, yet remarkably free of human error and inefficiency.
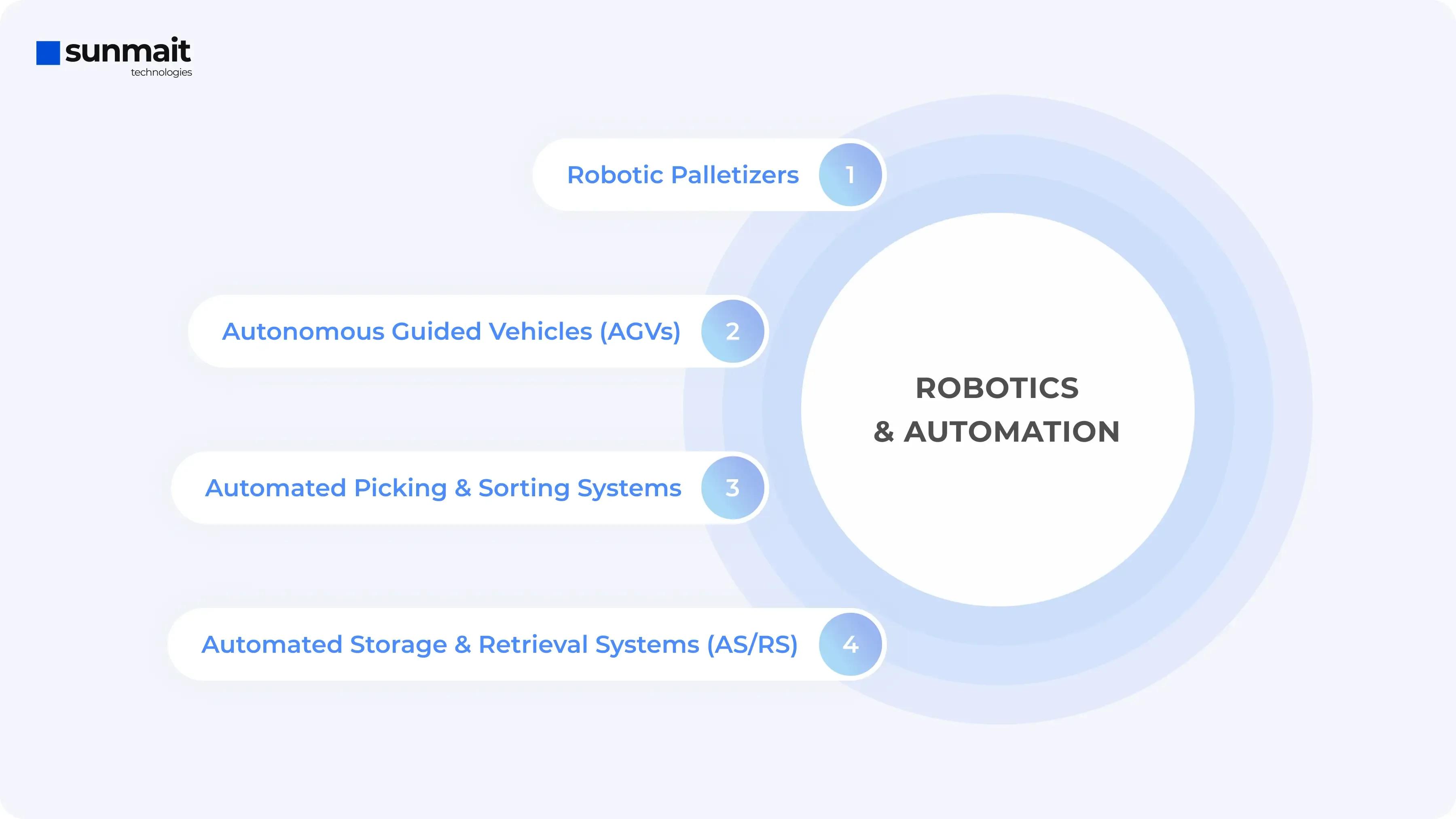
Robotics and Automation in Logistics
This transformation is driven by several key innovations:
Automated Picking and Sorting Systems: Picture robots swiftly navigating through warehouse aisles, picking items with precision and speed. Companies like Amazon use these automated systems to handle millions of orders daily, reducing processing times and minimizing mistakes. These systems can operate around the clock, ensuring that orders are fulfilled promptly and accurately.
Robotic Palletizers: In traditional warehouses, stacking products onto pallets is labor-intensive and prone to errors. Robotic palletizers automate this task, efficiently arranging products for shipment. These robots handle heavy lifting, reducing the risk of injury and improving overall safety. For example, in beverage distribution centers, robotic palletizers stack cases of drinks quickly and consistently, optimizing the use of space and ensuring stability during transport.
Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs): AGVs transport goods within warehouses and distribution centers without human intervention. These vehicles follow predefined paths using sensors and navigation systems. At the distribution center, you'll see AGVs moving pallets of products from storage to shipping, fitting right into the workflow. By handling repetitive transport tasks, AGVs free up human workers to focus on more complex activities.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): AS/RS maximize space utilization by using robots to store and retrieve items from high-density storage locations. Imagine a vertical warehouse where items are stored on towering racks. Robots navigate these racks, picking and placing items with incredible precision. This system not only saves space but also speeds up the order fulfillment process, as robots can quickly locate and retrieve items.
By incorporating these advanced technologies, logistics operations become faster, safer, and more cost-effective. Robotics and automation enhance productivity and reliability, creating a more efficient and responsive supply chain.
Blockchain Technology in logistics
By integrating blockchain, logistics operations become more secure, transparent, and efficient. The technology enhances trust among stakeholders, streamlines processes, and reduces the potential for fraud and errors.
Here’s how it impacts the industry:
Secure Data Exchange: Blockchain ensures that data is encrypted and securely exchanged, reducing the risk of data manipulation or unauthorized access. For example, a pharmaceutical company can securely track the production and distribution of medication, ensuring the data remains tamper-proof and authentic.
Transparent and Real-time Visibility: Blockchain provides a decentralized ledger that offers transparent and real-time tracking of goods. Every transaction is recorded and immutable, allowing all stakeholders to access accurate and up-to-date information about the movement of goods. A retailer, for instance, can track the journey of a shipment from the manufacturer to the store shelf, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Last Mile Delivery Innovations
Last mile delivery refers to the final step in the logistics process, where goods are transported from a transportation hub to the final delivery destination, typically the customer’s doorstep. This phase is critical as it directly affects customer satisfaction.
Innovations in Last Mile Delivery:
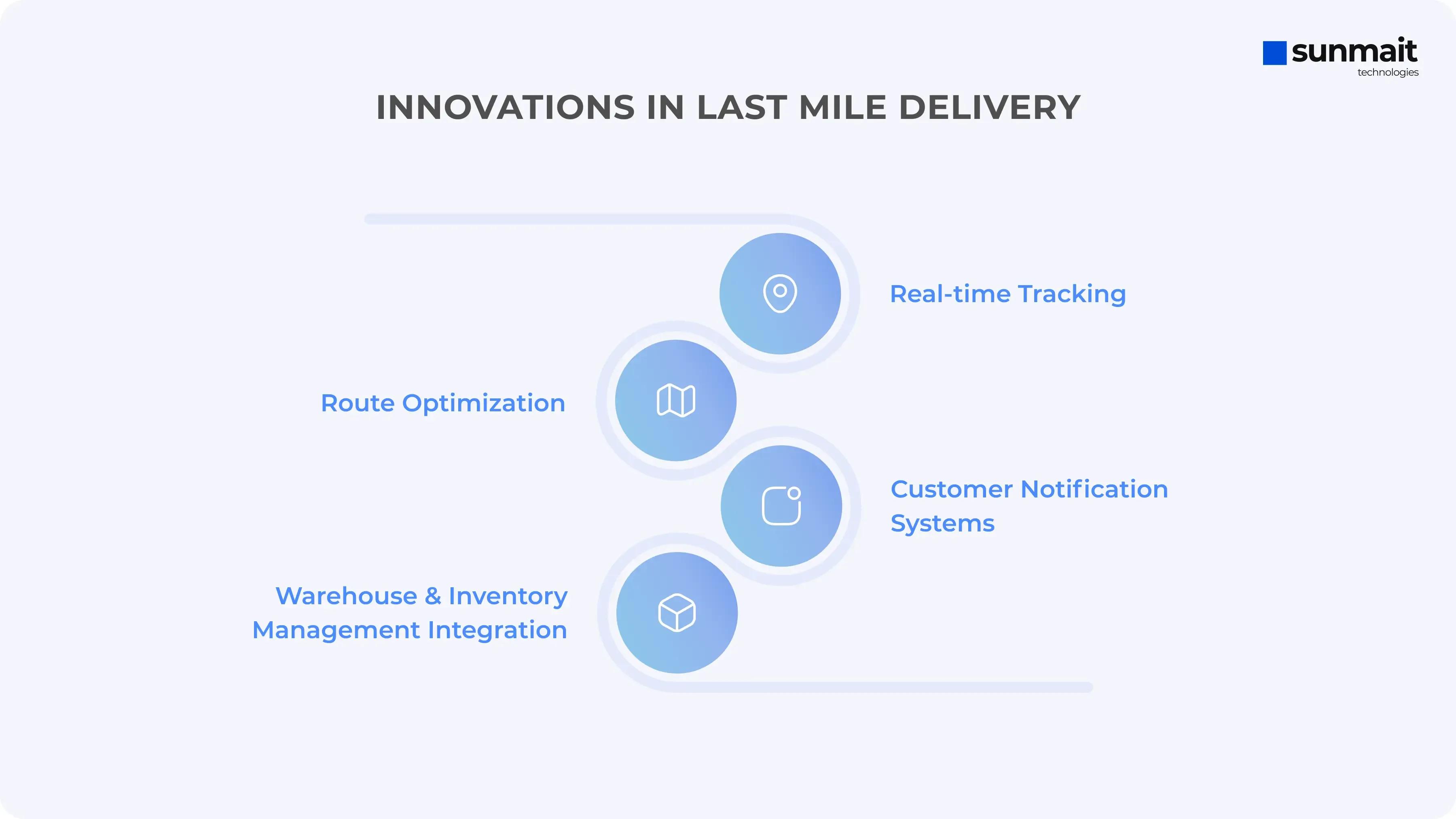
Innovations in Last Mile Delivery
Real-time Tracking: Customers can track their packages in real-time, knowing the exact location and estimated delivery time. For instance, companies like UPS provide a live map showing the delivery truck's location as it approaches.
Route Optimization: Advanced algorithms analyze traffic patterns, weather conditions, and other variables to determine the most efficient delivery routes. This reduces fuel consumption, delivery times, and costs, ensuring timely deliveries. FedEx uses route optimization software to dynamically adjust routes for their delivery vehicles.
Customer Notification Systems: Automated notifications keep customers informed about their delivery status through text messages or emails, providing updates on estimated arrival times and any potential delays. DHL offers real-time notifications, allowing customers to reschedule or redirect deliveries if necessary.
Warehouse and Inventory Management Integration: Seamless integration between warehouses and delivery systems ensures that inventory is managed efficiently and that items are ready for dispatch as soon as orders are placed. Amazon's fulfillment centers use advanced inventory management systems to ensure that items are picked, packed, and shipped quickly, reducing delivery times.
Examples of Last Mile Deliveries:
Drone Deliveries: Companies like Wing (a subsidiary of Alphabet) and Amazon Prime Air are using drones to deliver packages quickly and efficiently. For instance, Wing delivers small packages directly to customers' yards within minutes, bypassing traffic and reducing delivery times significantly.
SmartBoxes: Solutions like DHL's Packstations allow customers to pick up their deliveries from secure, automated lockers at convenient locations. This not only provides flexibility for customers who can’t be home to receive packages but also reduces the need for multiple delivery attempts.
Electric Cargo Bikes: Companies like UPS and DHL are deploying electric cargo bikes for urban deliveries. These bikes can navigate through traffic more easily than traditional delivery vans, reducing delivery times and emissions. For example, DHL uses electric cargo bikes in major European cities to deliver packages in a more sustainable way.
Robotic Couriers: Companies like Starship Technologies and Amazon are experimenting with small, autonomous robots that deliver packages directly to customers' doors. These robots can navigate sidewalks and even cross streets to complete deliveries, providing a futuristic and efficient delivery solution.
Crowdsourced Delivery: Platforms like Postmates and Uber Eats leverage a network of independent couriers to deliver packages and food items. This model allows for flexible, on-demand deliveries, often within an hour. For instance, Postmates uses a fleet of independent couriers to deliver a wide range of items from local stores and restaurants.
Here's what those innovations might look like:

Drone Deliveries
Innovations in last mile delivery are enhancing the speed, reliability, and transparency of the delivery process, leading to higher customer satisfaction and operational efficiency in logistics.
Digital Twins
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or systems that enable real-time monitoring, simulation, and optimization.
Given these environmental challenges, there is a growing trend towards sustainability in logistics. Companies are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices such as electric vehicles, route optimization, green warehousing, sustainable packaging, and carbon offsetting. This shift not only reduces the environmental impact but also meets the rising consumer demand for environmentally responsible business practices. Sustainable and green logistics are essential for a healthier planet and efficient supply chain operations.
Digital Twins
Here’s how they impact logistics:
Real-time Monitoring: Digital twins provide a live feed of the physical counterpart’s status, allowing for real-time tracking of inventory, machinery, and transportation vehicles. For instance, a digital twin of a warehouse can monitor environmental conditions like temperature and humidity, ensuring optimal storage conditions for perishable goods.
Simulation and Optimization: By creating a digital twin of a supply chain, companies can simulate various scenarios to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize processes.For example, a logistics company can use digital twins to test different routing strategies for delivery trucks. These simulations can consider various factors such as weather conditions, where strong winds or icy roads may cause drivers to slow down. Additionally, they can account for border congestion and other potential delays. A delay in one stage, like refueling, can have a cascading effect, impacting delivery times and overall efficiency. By breaking down these factors, companies can find the most efficient paths, minimize delays, and reduce fuel consumption.
Predictive Maintenance: Digital twins can predict when equipment or vehicles will need maintenance by analyzing real-time data and historical performance. This reduces downtime and extends the lifespan of assets. For example, a digital twin of a delivery truck can monitor engine performance and alert the maintenance team before a breakdown occurs.
Enhanced Collaboration: Digital twins facilitate better collaboration among stakeholders by providing a shared, accurate view of assets and operations. This transparency helps in making informed decisions quickly. For instance, suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers can all access a digital twin of the supply chain to coordinate their activities more effectively.
Improved Customer Experience: By using digital twins, companies can offer more reliable delivery times and enhanced service. For example, if a digital twin detects a delay in the supply chain, the company can proactively inform customers and adjust delivery schedules accordingly.
In summary, digital twins enhance the efficiency, reliability, and agility of logistics operations, leading to improved performance and customer satisfaction.

Sustainable and Green Logistics
Sustainable and Green Logistics
The logistics sector significantly contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and energy consumption. For instance, transportation is responsible for nearly 24% of global CO2 emissions from fuel combustion. (Source of data: Our World in Data )
Given these environmental challenges, there is a growing trend towards sustainability in logistics. Companies are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices such as electric vehicles, route optimization, green warehousing, sustainable packaging, and carbon offsetting. This shift not only reduces the environmental impact but also meets the rising consumer demand for environmentally responsible business practices. Sustainable and green logistics are essential for a healthier planet and efficient supply chain operations.
Here’s how these strategies are being implemented:
Eco-friendly Transportation: Companies are adopting electric and hybrid vehicles to reduce carbon emissions. For example, DHL is expanding its fleet of electric delivery vans to lower its environmental footprint.
Efficient Route Planning: Advanced route optimization software helps reduce fuel consumption and emissions by finding the most efficient delivery paths. UPS’s ORION system, for instance, has significantly cut fuel use by optimizing delivery routes. These software solutions not only plan the most efficient routes but also adapt in real-time to changes in traffic conditions, further reducing the carbon footprint.
Green Warehousing: Warehouses are being designed and operated with sustainability in mind, incorporating energy-efficient lighting, solar panels, and advanced insulation. To further enhance sustainability, warehouse management systems (WMS) now integrate energy management software that monitors and optimizes energy consumption, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and reducing overall energy costs. Amazon’s fulfillment centers, for example, use such integrated systems to help power their operations with 100% renewable energy by 2025.
Carbon Offsetting: Many logistics companies are investing in carbon offset programs to compensate for their emissions. For example, FedEx offers carbon-neutral shipping options where the emissions from shipping are offset by investing in environmental projects. Software tools are also being developed to calculate and manage carbon offsets, providing businesses with accurate data on their carbon footprint and the effectiveness of their offsetting strategies.
Supply Chain Collaboration: Working with partners and suppliers to ensure sustainable practices throughout the supply chain is critical. Collaboration platforms enable real-time communication and data sharing between partners, helping to reduce inefficiencies, optimize resource use, and ensure sustainability goals are met across the supply chain.
Packaging Innovation: Reducing packaging waste through the use of recyclable and biodegradable materials is a key focus. Companies like IKEA are using flat-pack designs and sustainable materials to minimize waste and enhance recyclability.
By integrating these practices, companies are not only reducing their environmental impact but also often achieving cost savings and meeting the growing demand for sustainable business operations. Sustainable and green logistics contribute to a healthier planet while maintaining efficient and effective supply chain operations.
Elastic Logistics
The use of advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, cloud computing, and blockchain, as described earlier, is precisely what enables companies to adhere to the principles of elastic logistics. These technologies, which are at the forefront of logistics trends for 2024, provide the flexibility, scalability, and real-time responsiveness needed to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and consumer demands.
To illustrate this, let’s consider the supply chain of a large e-commerce retailer, such as Amazon, during the holiday season. As the holiday season approaches, consumer demand spikes dramatically. Elastic logistics allows Amazon to scale its operations quickly to meet this surge. The process begins with demand forecasting, where AI algorithms analyze historical data and current trends to predict the volume of orders expected during this period. Based on these predictions, Amazon adjusts its inventory levels by rapidly increasing stock in key fulfillment centers closer to major customer hubs. This ensures that popular items are readily available and can be shipped quickly.
Next, warehouse operations are optimized. Amazon’s dynamic warehousing approach means that additional temporary storage facilities can be leased and set up as needed. Inside these warehouses, robotic systems are deployed to handle the increased workload efficiently, picking and packing orders at a much faster rate than would be possible manually.
As orders are processed, route optimization tools come into play. Using real-time traffic data, weather conditions, and delivery locations, AI systems calculate the most efficient delivery routes for Amazon’s fleet of delivery trucks and vans. This not only speeds up delivery times but also reduces fuel consumption and costs, which is particularly important when operating at such a large scale.
During this peak period, flexible labor management is also crucial. Amazon brings in temporary workers and adjusts shifts dynamically to ensure that enough personnel are available to handle the increased volume of orders. If certain fulfillment centers are overwhelmed, resources can be reallocated in real-time, ensuring that the entire supply chain remains balanced and responsive.
Finally, customer satisfaction is maintained through the seamless integration of these systems. Real-time tracking allows customers to monitor their orders from the moment they are placed until they arrive at their doorstep. If delays or issues arise, automated systems can immediately notify customers and offer solutions, such as rerouting packages or providing alternative delivery options.
Using this example, we can see that flexibility, scalability, and real-time responsiveness to the fluctuating demands of customers are some of the most important principles that ensure a complex supply chain adapts efficiently and effectively. This not only ensures the optimization of resources, which reduces costs, but also assures high levels of customer satisfaction even in the busiest times of the year.
Conclusion
The logistics industry is fast evolving in its quest for increased efficiency, sustainability, and responsiveness. Principal technologies which drive this change include AI, IoT, blockchain, and robotics, further enabling elastic logistics, real-time tracking, and green logistics practices. Such innovations will not only help improve operational efficiency but also make a major impact on improving customer satisfaction and lowering environmental impact.
At Sunmait Technologies, we realize the role these innovations have come to play in modern logistics. With years of rich experience in developing customized solutions across different domains, we help businesses put into motion state-of-the-art technologies that will optimize their supply chain operations. Be it through advanced demand forecasting systems, dynamic warehousing solutions, or sustainable logistics practices, Sunmait Technologies is always there to push the future of logistics forward.
In partnering with us, companies can use our expertise to forge ahead in today's competitive market and make sure they're not just able to conquer the logistical challenges of today but also be better positioned for the demands of tomorrow.



